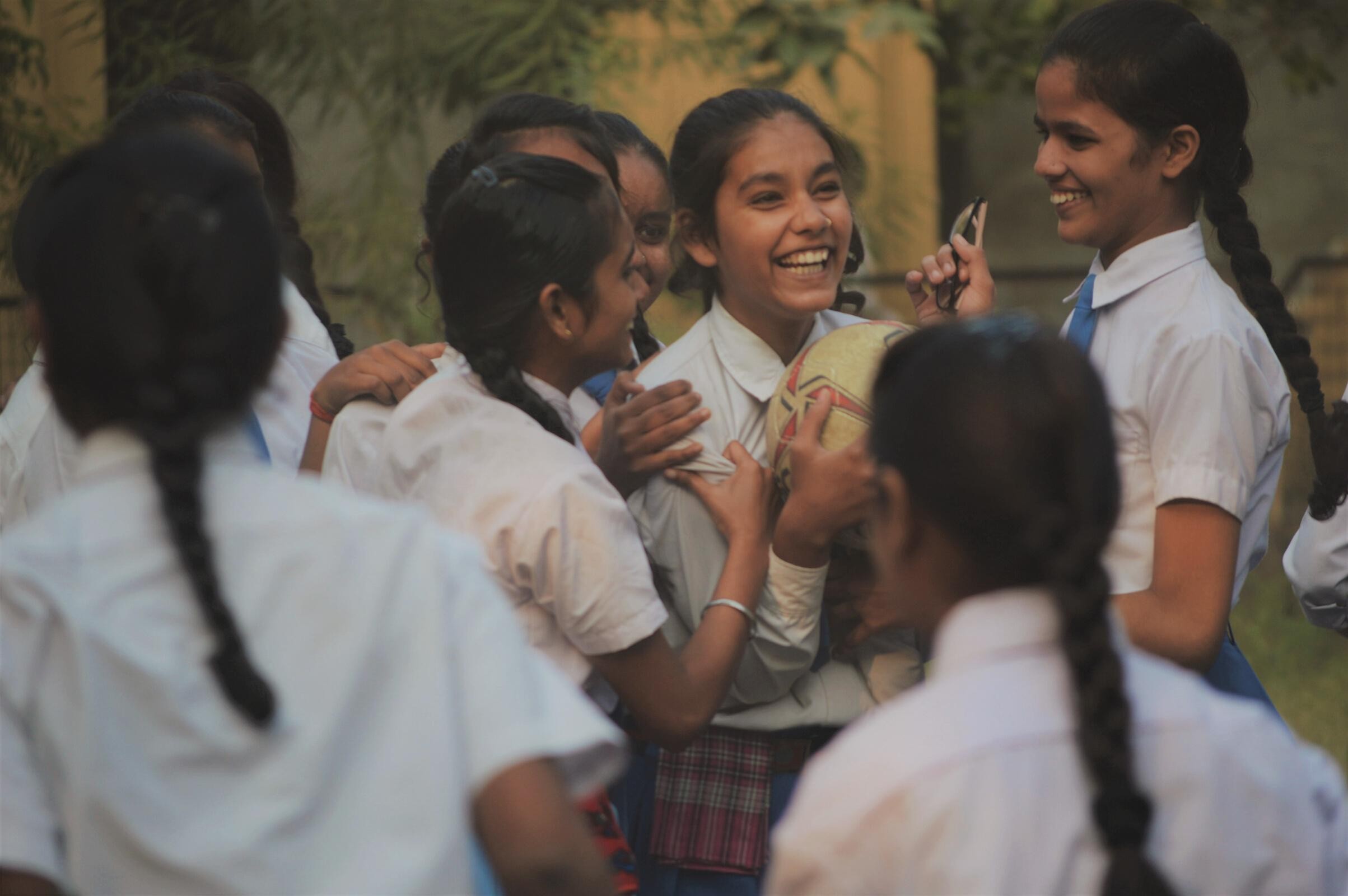
Global Reach
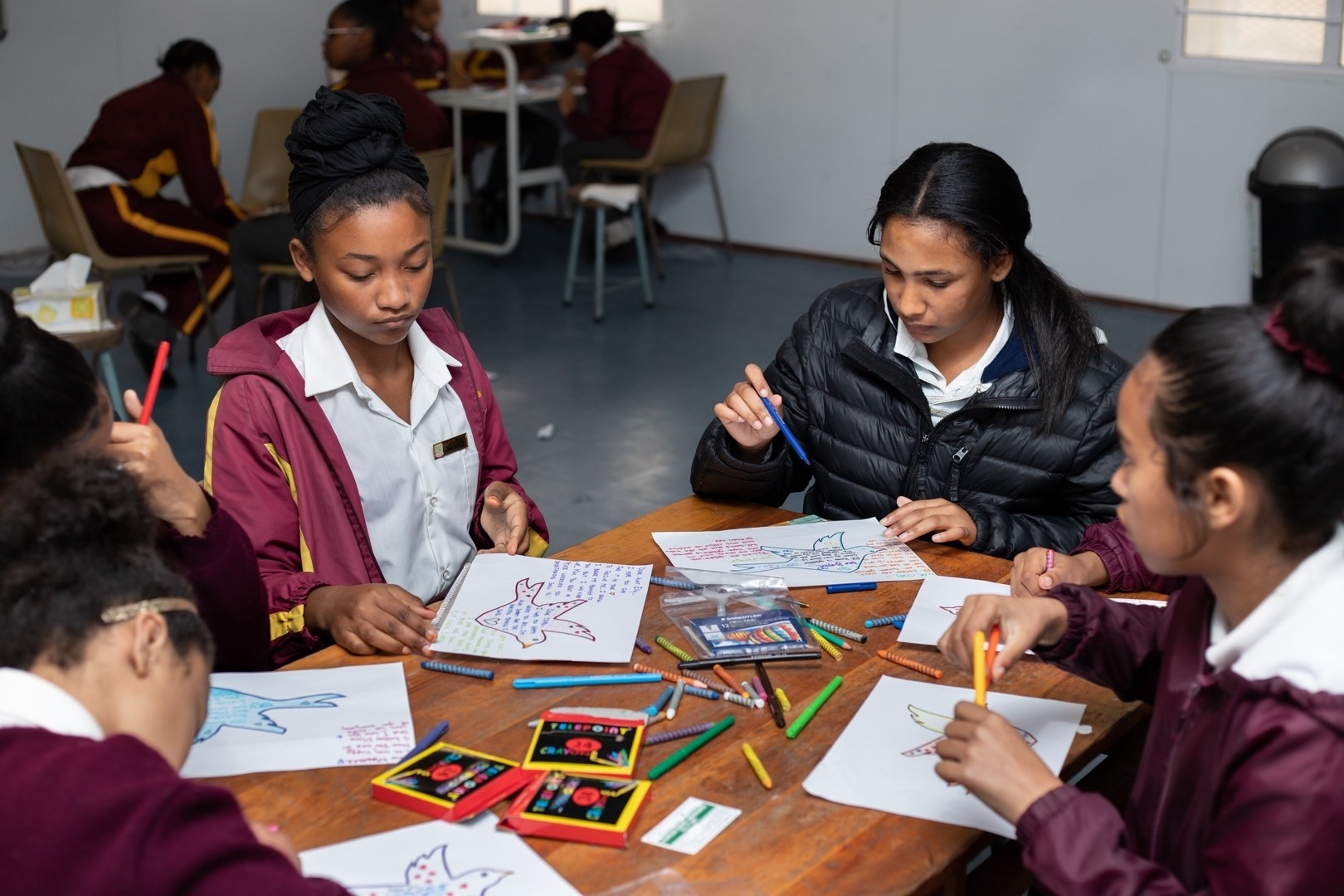
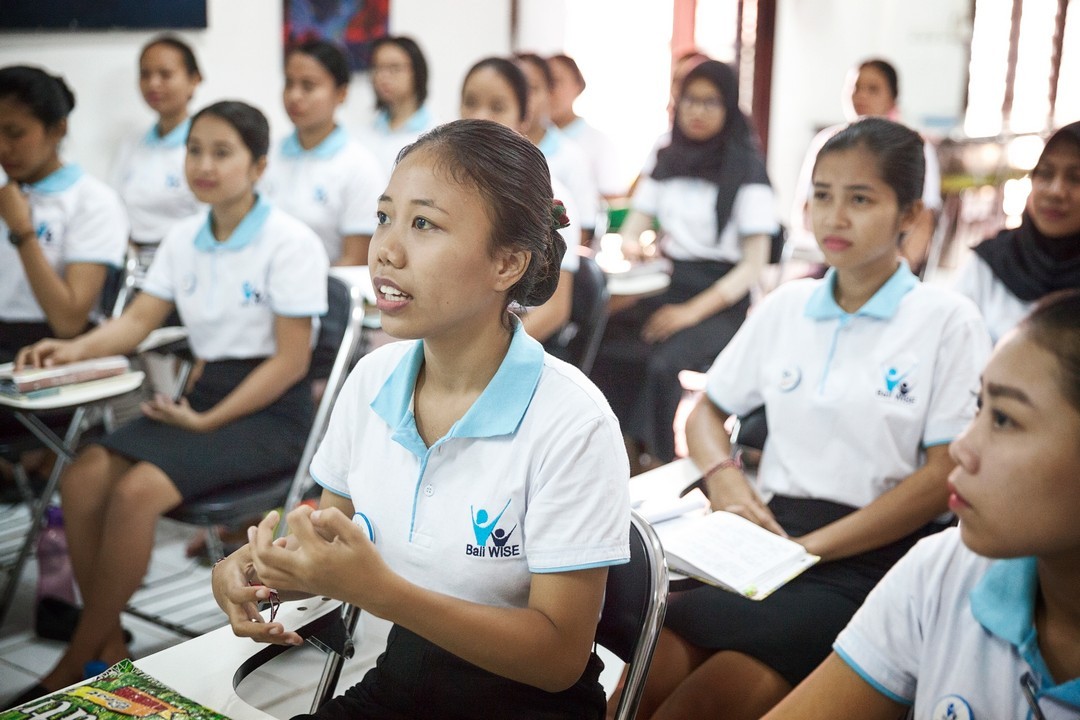
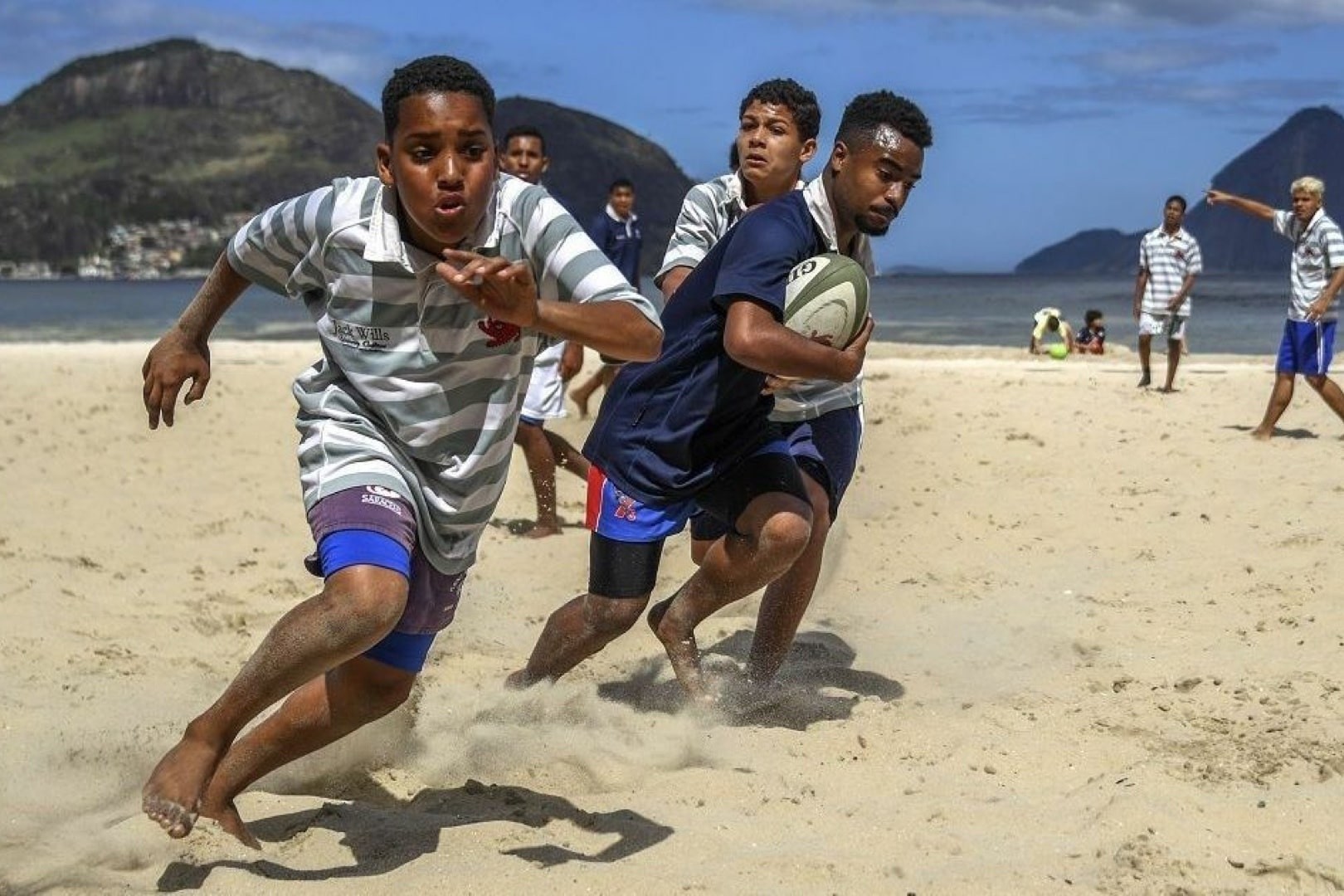
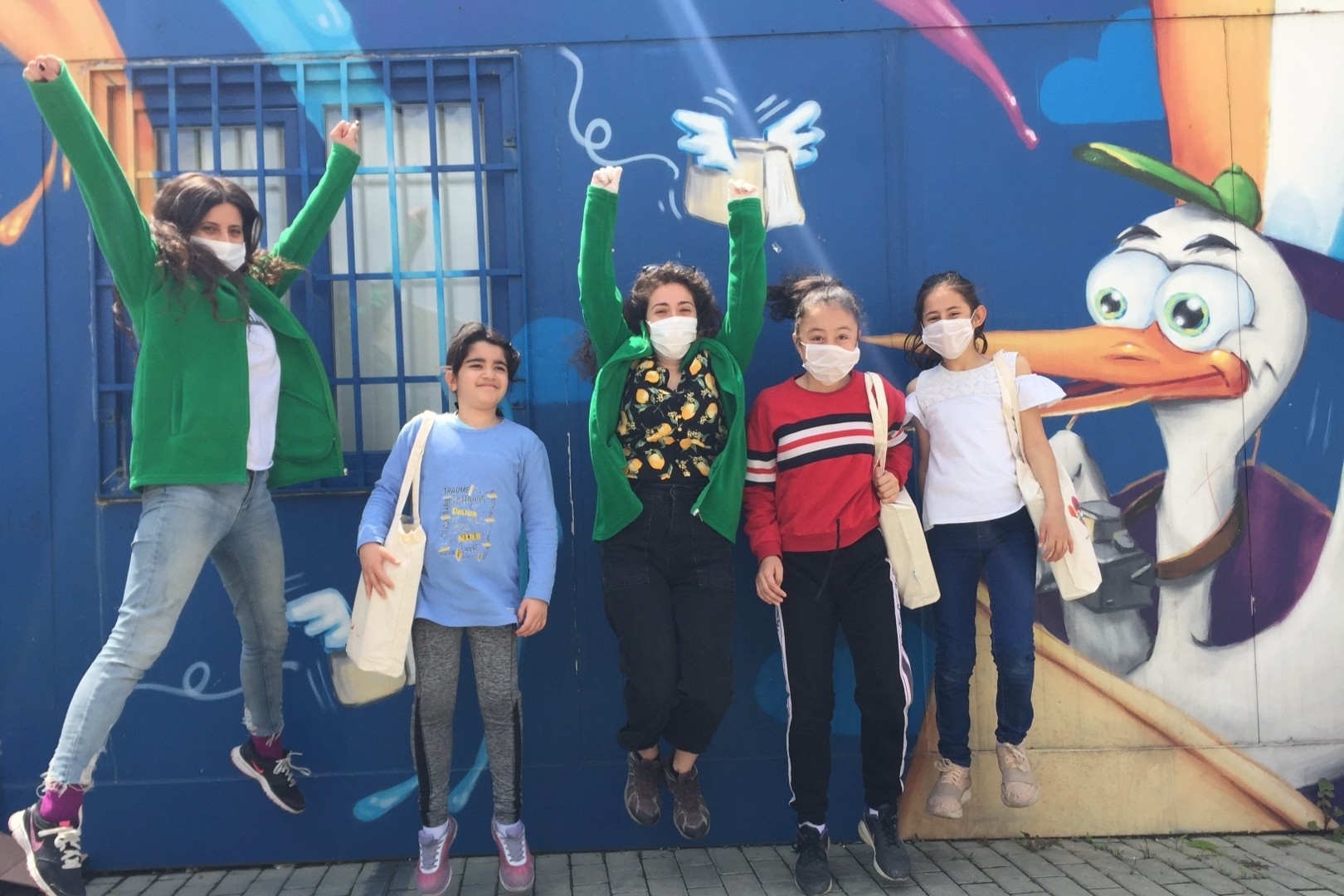
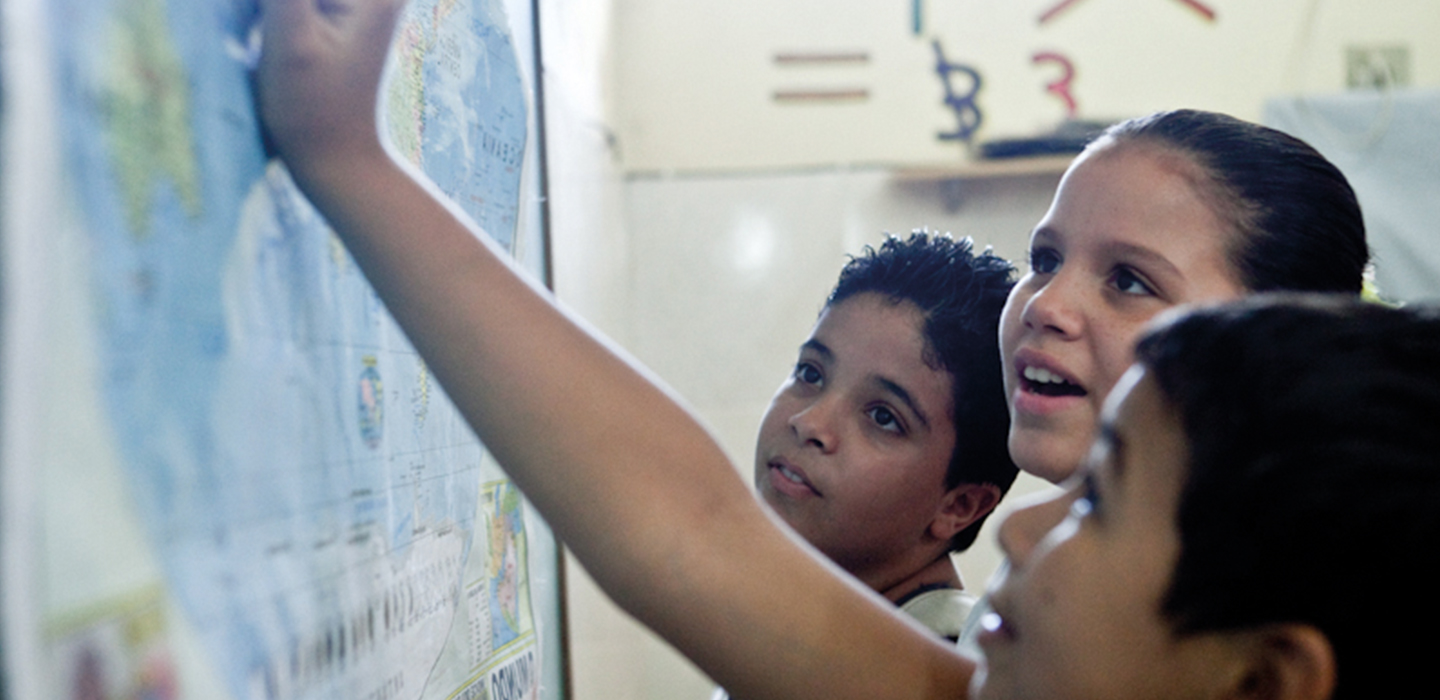
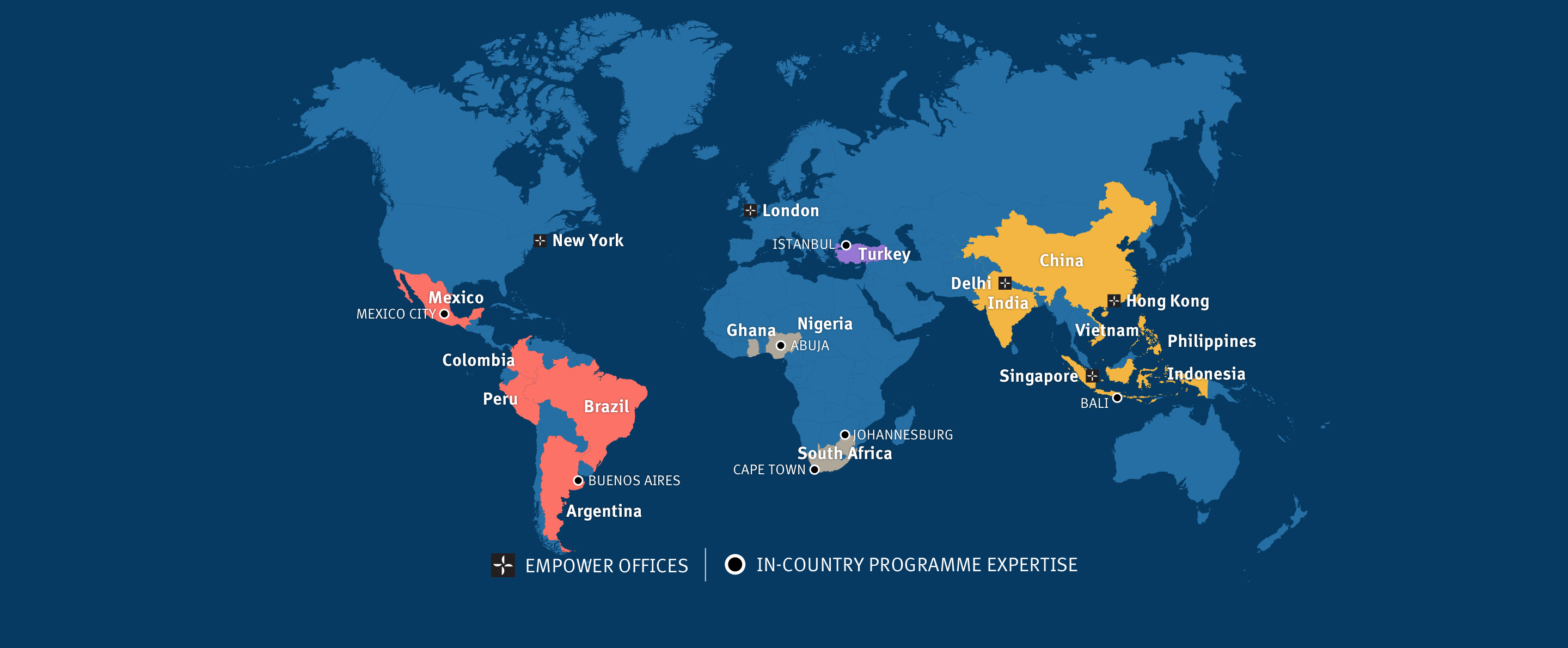
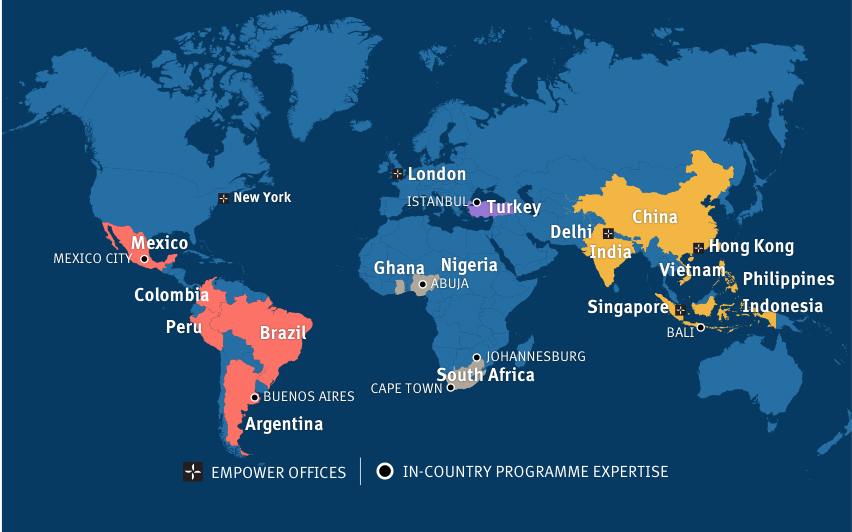
We currently support 150 local organisations across 15 emerging markets. We have offices in 5 countries and programme staff/consultants in 4 other countries—supporting effective and innovative programmes that enable marginalised young people to flourish.
1,465
Grants Made
$50 Million
Awarded
1 Million
Youth Directly Impacted
3.5 Million
Lives Touched
Select a region or country to learn more
Connect with EMpower
Stay up-to-date on the latest EMpower news, highlights from our grantee partners, upcoming events, and more.
Make a Difference with EMpower
Our Board Directors and the Leadership Council underwrite all of our Management, General and Fundraising expenses, so 100% of your donation goes directly to empowering marginalised young people.